In the last decade, Africa has experienced a significant surge in internet usage, reshaping how individuals across the continent communicate, work, and access information. This transformation has been fueled by the widespread adoption of mobile technology and substantial investments in internet infrastructure, leading to a growing number of Africans connecting to the digital realm.
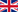
According to Statista, the internet landscape in Africa has undergone rapid evolution, with approximately 570 million users recorded in 2022. Nigeria leads the continent with over 100 million users, followed by Egypt with 76 million and South Africa with 41 million. This surge in internet usage is attributed to improved telecommunication infrastructure and increased adoption of mobile devices.
Central to this evolution are social media platforms, which serve as vital connectors for social interactions and business engagements. According to Statista, Africa’s social media users have continuously increased, totaling over 384 million as of 2022. Social media penetration is significantly higher in Northern and Southern Africa compared to other regions. Despite notable progress, persistent challenges such as inadequate infrastructure, high data costs, and disparities in digital literacy continue to hinder universal internet adoption.
Nevertheless, concerted efforts are underway to tackle these obstacles through initiatives focusing on infrastructure expansion, governmental policies, and international collaborations. As the reach of internet connectivity expands, it carries the potential to catalyze economic development, spur innovation, and enhance the quality of life for millions of Africans.
The latest data from the International Telecommunication Union's "Facts and Figures 2023" report indicates that internet penetration in Africa stood at 37% in 2023, marking a slight decrease from the previous year's 40%. However, a consistent upward trajectory in internet adoption over the past decade highlights the resilience and promise of Africa's digital future.
From a modest 16% in 2013, internet usage in Africa climbed to 25% by 2016 and continued to grow steadily, reaching 40% in 2022. The only other decline over the past ten years occurred in 2017, with usage dropping by 3.3 percentage points. Several factors contributed to the surge between 2020 and 2022, notably the COVID-19 pandemic, which forced many activities online, thereby increasing internet usage.
While the ITU does not provide specific reasons for the decrease between 2022 and 2023, several factors could be responsible, including the resumption of physical activities, internet blackouts in certain countries, and access issues elsewhere. In August 2023, disruptions in internet service in some African countries were attributed to the cutting of the WACS and SAT-3 submarine cables.
Challenges and Opportunities for Internet Expansion
Despite the progress, there's significant room for improvement in Africa's internet connectivity compared to global averages. While the continent reported a 37% internet usage rate, the global average stood at 67%. Meanwhile, Europe, the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS), and the Americas recorded internet usage rates between 87 and 91%. The Arab States and the Asia-Pacific region are closer to the global average, with rates of 69% and 66%, respectively.
Enhanced connectivity could significantly boost various economic sectors in Africa, particularly e-commerce. According to TechCabal Insights' "Future of Commerce: Outlook for 2024" report, the e-commerce sector is booming, with total revenue reaching $32.49 billion in 2022 and 387.5 million African online shoppers.
Despite having 25 submarine cables and 1.2 million km of terrestrial fiber, Africa's optical fiber footprint remains limited, with many countries lacking the necessary high-speed telecommunications infrastructure. Additionally, Africa has the highest fixed broadband access rates in the world, costing an average of 14.8% of Gross National Income (GNI), far above the ITU's recommended 2%.
To address these challenges and enhance internet access in Africa, the Internet Society has made several recommendations. These include reforming the telecom market to encourage the emergence of competing access networks and expanding national basic infrastructure beyond major submarine cable landing points and primary population centers to additional population hubs.
Despite grappling with various challenges, with affordable access to the internet standing out as a primary concern, Africa remains resolute in its commitment to prioritize internet connectivity and accessibility. The continent's digital landscape is in a state of continual transformation, lifted by the increasing demand for connectivity and the promising opportunities it presents for stimulating economic growth. Through concerted collaborative efforts aimed at narrowing infrastructure gaps and improving affordability, Africa is poised to fully leverage the internet's potential to drive its development and prosperity forward.