In the past few years, satellite communication has remained standalone technology, independent of mobile networking. But today, it has come a long way improving its technical performance and capabilities as well as becoming much more competitive to match terrestrial offers. The next generation of satellites – built from 5G architecture – will integrate with networks to manage connectivity to cars, vessels, airplanes and other IoT devices in remote and rural areas. The emerging 5G vision opens a new chapter in communications and offers the possibility to consider satellite communication alongside and in combination with terrestrial solutions.
5G satellite communication market is expected to witness a high growth, owing to the increase in the number of communication satellite constellations for the support of 5G systems across the globe.
Furthermore, the emergence of 5G satellite communication services for IoT is expected to gradually increase the demand for 5G satellite communication across the world. Having billions of IoT devices poses a significant operational challenge. To combat on-going security vulnerabilities, devices need constant updates and future 5G devices will require an efficient distribution of data on a global scale. With wide coverage and broadcast capabilities, satellites are well-positioned to support IoT. They can offer shared uplink connectivity for a massive amount of IoT devices and provide data aggregation.
With an integrated satellite-terrestrial solution, the additional capacity can be used as an IoT backup or supplementing congested data traffic. This permits higher peak rates and more reliability in massive machine communication.
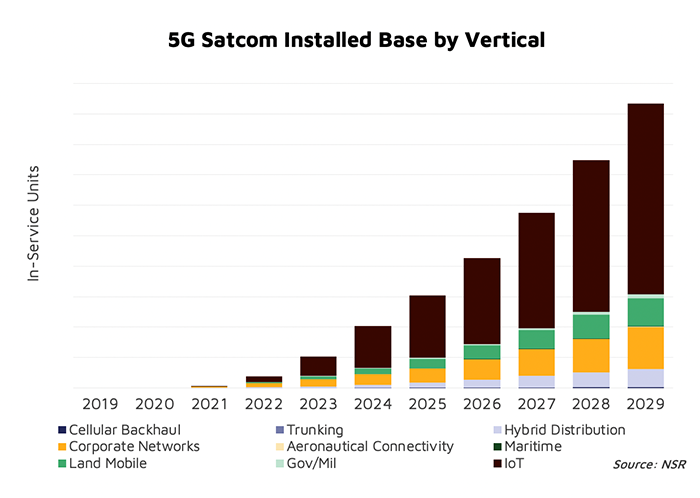
In addition, the increasing demand for satellites for different business verticals and the need to resolve the bandwidth problem in the current network are some of the major factors expected to create lucrative opportunities for the global 5G satellite communication market in the coming 10 years.
The Global 5G Satellite Communication Market report projects the market is expected to grow at a significant CAGR of 28.91% on the basis of value during the forecast period from 2021 to 2030. This global market has gained widespread importance, however, issues related to the spectrum allocation and backhaul connectivity are some of the factors that are restraining the market growth.
Global 5G satellite communication market segmentation
The 5G satellite communication market is segmented on the basis of orbit (GEO, MEO, and LEO), spectrum, end user, satellite solutions, and region.
Traditional communication satellites are geostationary and have been in orbit for more than 50 years. GEO satellites weigh more than 1000kg and operate 36,000 kilometers above the earth. These satellites remain in a fixed position relative to any position. Despite Earth’s orbit, this allows ground-based antennas the ability to point directly at the satellite, in a fixed position.
In contrast, Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites are miniaturized, orbiting versions that operate between 500 and 2000 kilometers above Earth’s surface and weigh under 500kg. Due to its low orbit, latency is significantly reduced as the satellite is better positioned to quickly receive and transmit data. Unfortunately, this also creates a smaller coverage area so LEO satellites continuously hand off communication signals and traffic across a constellation of satellites. This ensures seamless, wide-scale coverage over a pre-defined geographical area.
The Low Earth Orbit (LEO) segment is expected to dominate the global 5G satellite communication market in 2021 and is anticipated to maintain its dominance throughout the forecast period 2021-2030.
Role of satellite in 5G
Satellite can play major roles in 5G within different areas, namely:
- Coverage expansion
- Backhauling services to fixed or moving base stations
- Complementing connectivity for mobile devices (ships, vehicles, trains, planes)
- Multi-gigabit per second data rates for enhanced mobile broadband
- Offloading a temporarily congested network
- IoT/M2M
- Spectrum sharing
- Resilience, security and availability
- Providing emergency response/disaster recovery communications
However, its development is not without challenges such as latency minimization, spectrum scarcity, energy consumption reduction, localization and integration issues, QoE guarantee, and supporting multiple heterogeneous services such as IoT/M2M and high rate video services.
The demand for satellite data services is increasing significantly, owing to increasing interest from the private sector toward the space industry. In June 2020, SpaceX launched 58 Starlink satellites and 3 small Earth-observation satellites. These 3 satellites and 12 other satellites provide views of earth’s surface that are consistently covered in sunlight. Moreover, in June 2020, Hong Kong Aerospace Technology Group (HKATG) signed a strategic partnership agreement with China Great Wall Industry Corporation (CGWIC). The cooperation includes joint development of the Golden Bauhinia constellation system design, R&D, satellite design, testing, launch, and in-orbit delivery. Such increasing participation of private players in satellite launches and increase in the number of satellites in the earth’s orbit enable satellite data and imagery service providers to provide their solutions for commercial purposes. For instance, in 2018, more than 90 satellites were launched for commercial purposes by the U.S., Italy, China, Japan, and the UK.
In Africa for example, over 30% of the African population live in landlocked countries, many in remote rural areas. Millions of Africans therefore experience significant challenges with access to reliable connectivity every day. According to Northern Sky Research (NSR) countries in sub-Saharan Africa are increasingly connected to the mobile internet. However, in 2019, there were 520 million people that did not use mobile internet and another 270 million who did not live within the footprint of a mobile network. Simply put, better solutions are needed as the number of connected devices and demand for bandwidth-intensive applications continue to soar across the continent.
In response to the ever-present digital divide in not only Africa, but the world, SES, the leader in global content connectivity solutions, has developed O3b mPOWER – a revolutionary non-geostationary orbit (NGSO) satellite-enabled communications system operating 8,000km away from earth. Due to launch in Q4 of 2021, O3b mPOWER will boost connectivity across the region by delivering connectivity services ranging from 50Mbps to multiple gigabits per second, offer unprecedented flexibility and reach, making it possible to optimize a network’s ability to scale to cloud, deliver bandwidth when and where it is needed, in real-time, using the flexibility of the system and the software-based architecture, support a massive increase in the backhaul capacity for 4G and 5G deployments and enterprise applications, allow for digital transformation, rapid cloud adoption and e-banking services; and more importantly will work towards tangibly bridging the digital divide.
Satellite communications is part of everyday life and has enormous benefits including reaching otherwise unreachable, underserved rural communities.
